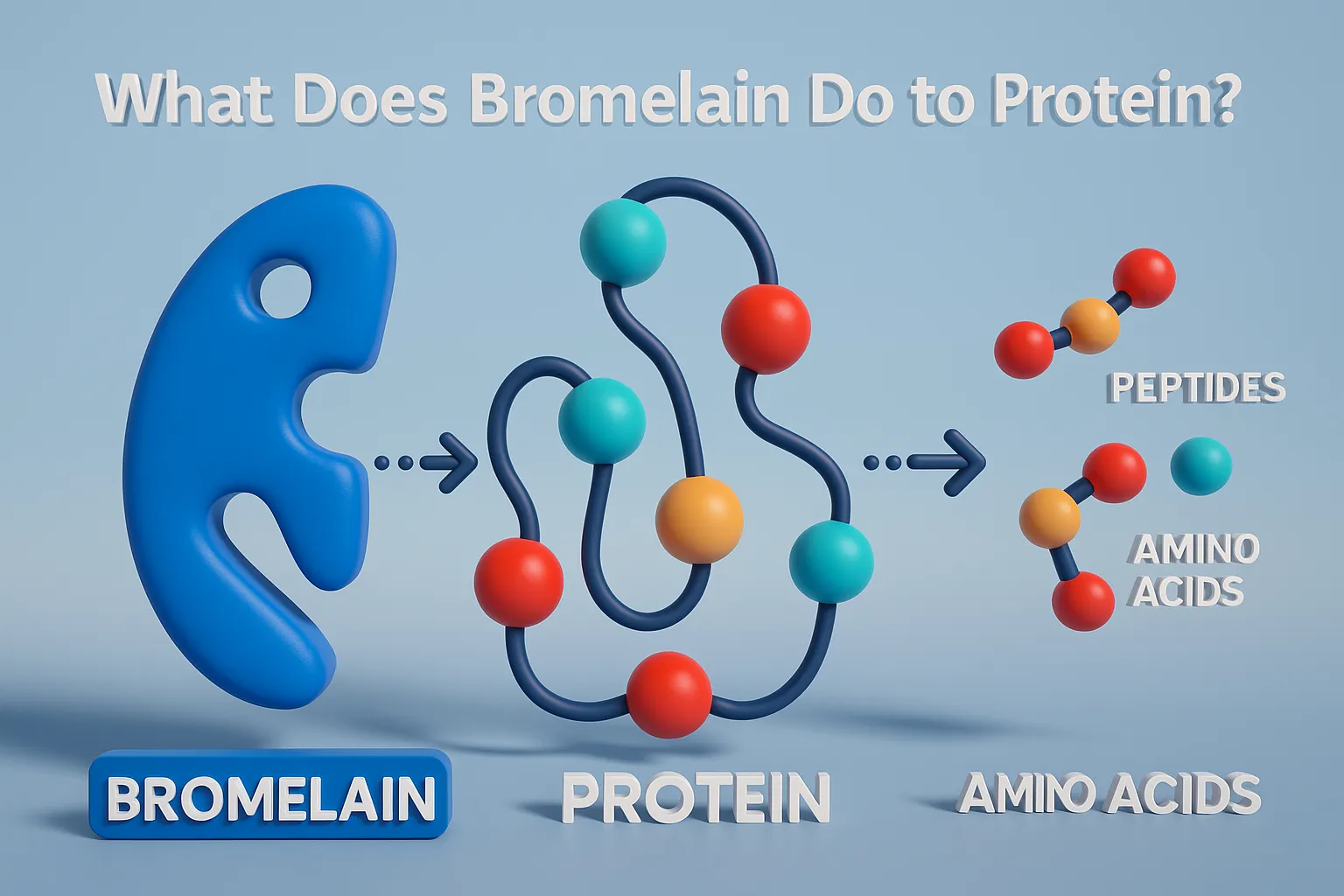
What does bromelain do to protein?
Bromelain is a powerful proteolytic enzyme, meaning it helps break down proteins into smaller building blocks like peptides and amino acids. This process is essential for:
Key Functions of Bromelain on Protein
- Digestion: Bromelain aids in digesting proteins in the stomach, making nutrients easier to absorb.
- Muscle Recovery: By breaking down damaged proteins in muscle tissue, bromelain supports faster recovery after exercise or injury.
- Anti-Inflammatory Action: It breaks down inflammatory protein complexes, helping reduce swelling and pain.
- Wound Healing: Protein breakdown by bromelain helps clear dead tissue and promotes regeneration.
How It Works
Bromelain acts on the peptide bonds in protein molecules. By cleaving these bonds, it converts large, complex proteins into smaller chains and free amino acids, which are more bioavailable to the body.
FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions
Does bromelain help with muscle soreness?
Yes. By breaking down damaged proteins and reducing inflammation, bromelain can help speed up muscle recovery and reduce soreness after workouts.
Is bromelain a protein itself?
Yes. Bromelain is a type of protein classified as an enzyme. It catalyzes the breakdown of other proteins without being consumed in the process.
Can bromelain improve digestion?
Absolutely. Bromelain enhances protein digestion, making it beneficial for people with digestive issues or low stomach acid.
Is bromelain effective on cooked proteins?
Yes, but cooking may deactivate bromelain itself. That’s why supplements or raw pineapple (especially the core) are better sources.